This blog post continues the security theme with a focus on Homomorphic Encryption, a technology that can perform computations and analytics directly on encrypted data without requiring plain decrypted data.
The topic of security and encryption has been on our radar for a long time, and we discussed it in relation to AI Security, Quantum Security, and other touchpoints in the past. This blog post continues the security theme with a focus on Homomorphic Encryption, a technology that can perform computations and analytics directly on encrypted data without requiring plain decrypted data.
The Need for Analytics with Encrypted Data
With ever-increasing cyberattacks, it is important that companies start applying Zero Trust models and become more proactive about cybersecurity threats. The increased threat is also leading to more awareness around general data privacy considerations and data privacy regulations. For example, GDPR has significant regulations when it comes to data privacy and data processing. The rise of cloud computing and specifications in businesses also accelerates data processing outsourcing. This requires strict regulations since client data is being handed over to a third-party data processor which is increasing the risk of data leaks. Ideally, the data would be handed over in an encrypted state so that third-party data processors don’t receive the plain unencrypted content, but unfortunately, that counteracts the purpose of the analytics processing.
This is where Homomorphic Encryption provides a benefit since the computations and analytics run directly on the encrypted data without having to decrypt it first. Third-party data processors can then work with encrypted data while having no knowledge about the data or the results. With the growing demand for data processing for privacy-critical data and strong privacy laws as well, the need is there. In fact, analysts believe future SaaS offerings will leverage Homomorphic Encryption as a core technology: “We believe homomorphic encryption will be a core technology for many future SaaS offerings to ensure the protection and privacy of data between third-party data processing and analytics providers. The dominant use case will be eliminating the current need to exchange and store data between business partners, third-party analysis firms or other extended data analytics solutions.”
Strong Privacy and Cybersecurity are a Minimum Standard
The importance of privacy and security for business leaders is pretty clear these days with increasing fraud, breaches, hacker attacks, and various other cybersecurity topics. According to a Forrester2 report, consumers are also becoming more security-conscious. “62% of US and 55% of UK consumers say that how a company handles their personal information is important to their purchasing decisions.” Therefore, customer data needs to be stored and handled securely to ensure no data breaches occur. This applies even more to third-party data processors.
The Healthcare industry in particular has experienced an increase in cyberattacks since the onset of COVID-19, as Forrester reports3. The reasons are mainly due to the introduction of virtual health models and remote patient monitoring devices with the expansion of third-party relationships. For example, AI-assisted clinical decision support services have been integrated with hospital systems that are performing remote analyses on patient data. Applying Homomorphic Encryption is one potential solution, but healthcare organizations must also invest in strategies to secure the entire organization. Applying a Zero Trust framework ensures security and privacy holistically is the foundation.

Wishful Thinking or Reality?
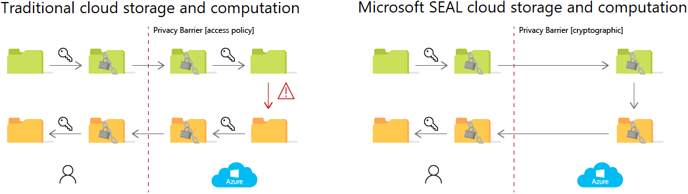
While there are certain limitations for near-term adoption of this technology like complexity, performance issues, and a lack of standardization, there’s little doubt about the benefits. In fact, implementations are already happening today. The Microsoft Azure SEAL library is an open-source software library that allows computation directly on encrypted data, making it easier to apply the potential of the cloud for privacy-critical data. Microsoft is pointing out a few considerations when leveraging the SEAL library, most importantly that only certain arithmetic computations are possible on
encrypted data. Microsoft SEAL allows additions and multiplications on encrypted integers or real numbers using two homomorphic encryption schemes. The BFV scheme is made for arithmetic operations with encrypted integers. The scheme CKKS supports additions and multiplications on encrypted complex or real numbers which provide approximate results, so it’s good for summing up encrypted real numbers, evaluating machine learning models, or computing distances of encrypted locations. The BFV scheme is the right choice when exact results with integer numbers are desired.
Another limitation is the required performance overhead for homomorphic encryption and the size of encrypted data. Apache Spark together with hardware acceleration can mitigate these scalability challenges and make homomorphic encryption more efficient. In the below Databricks talk by Microsoft’s Kim Laine, you can learn more about SEAL and see what the performance can be when complex computations and encrypted data are executed in Spark.
Where to get started?
Valorem Reply and the global Reply network are here to help with our experienced teams of security, analytics and cloud experts that can meet you wherever you are on your analytics and security journey. If you have a security project in mind or would like to talk about your path to security, we would love to hear about it! Reach out to us at marketing.valorem@reply.com to schedule time with one of our experts.







